You’ve highlighted the crucial role that temperature control plays in data center management, especially in preventing condensation and potential damage to equipment. Like indirect air cooling and indirect evaporative cooling (IEC), are key strategies for maintaining the right environmental conditions. Let’s break down how each of these approaches contributes to the overall efficiency and sustainability of data centers:
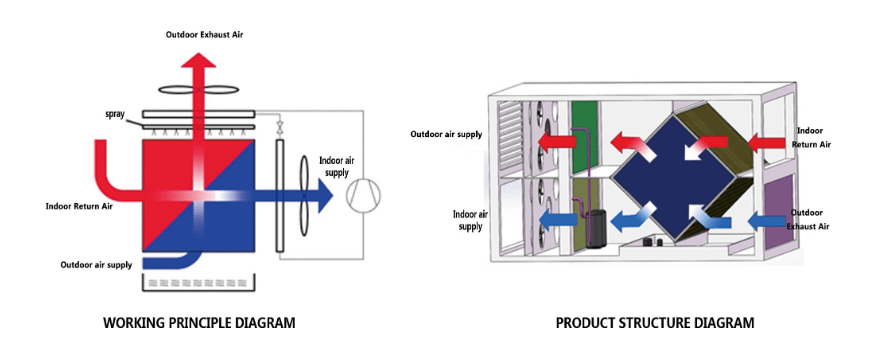
1. Indirect Air Cooling
- Key Benefits: Indirect air cooling uses external air to cool the interior of a data center without allowing contaminants or humidity from outside to enter. This is particularly valuable in environments where external air quality could impact the system’s performance.
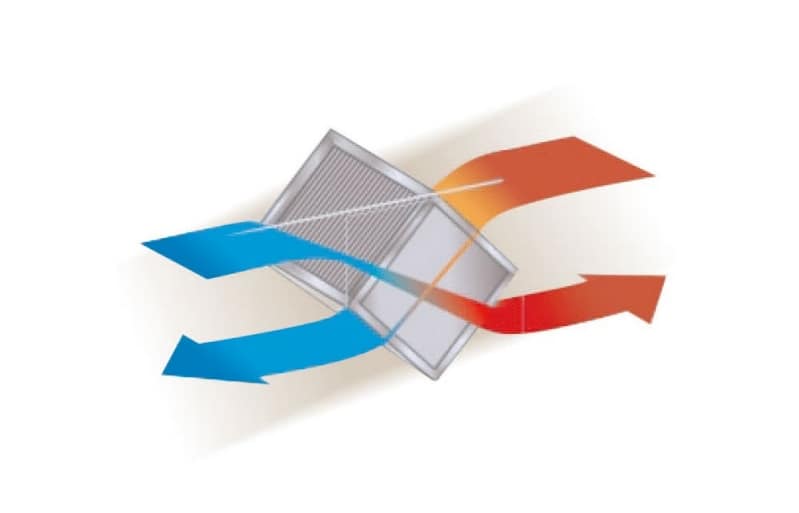
- Heat Exchanger Role: The air-to-air heat exchanger acts as a barrier, keeping the interior and exterior air streams separate while still allowing heat to transfer. This ensures a clean, controlled environment inside the data center while leveraging the ambient outdoor air for cooling.
2. Indirect Evaporative Cooling (IEC)
- Why It's Effective: IEC works by spraying water on the ambient air side of a heat exchanger, which cools the incoming air through an evaporative process. This can lead to significant temperature reductions, especially in warm, dry climates.
- Energy Savings: As you pointed out, IEC can reduce the temperature inside the data center by 6-8°C (10-15°F) during summer conditions. The energy savings—up to 28% over conventional free cooling and 52% over air-cooled alternatives—make it an attractive option for reducing operational costs.
3. Dry Cooling
- When It’s Sufficient: In areas where ambient temperatures are consistently low, dry cooling can often provide enough cooling capacity without needing water. It relies on natural airflows to cool the system, reducing complexity and maintenance needs.
4. Plate Heat Exchangers for Evaporative Cooling
- Cross-Flow Heat Exchangers: As part of the evaporative cooling system, cross-flow plate heat exchangers offer high efficiency and low pressure drops, which is essential for maintaining the required airflow and ensuring reliable heat transfer. Their corrosion protection and water-tightness further ensure longevity and reliability.
- Environmental and Cost Efficiency: By integrating these heat exchangers into the cooling system, data centers can not only cut energy consumption but also contribute to sustainability goals. Using water in a controlled, evaporative manner minimizes water usage compared to traditional cooling towers, which is important for areas facing water scarcity concerns.
Summary of Benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: Reduced operational costs through energy-efficient cooling methods.
- Environmental Impact: Lower carbon footprint by using passive cooling strategies and water-efficient technologies.
- Reliability and Longevity: Reduced risk of condensation and equipment damage, ensuring continuous uptime.
Incorporating these advanced cooling methods into data centers can help operators balance efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability while maintaining the required performance standards.